This study conducted a comparative bibliometric analysis of block-scale walkability research based on agent modeling (ABM) in China and abroad from 2015 to 2024. With the help of tools such as VOSviewer, it revealed the differences in research trajectories, methodological paths, and institutional logic between the two. Chinese research shows policy-driven characteristics, especially driven by the "15-minute community living circle" policy, focusing on community renewal, aging-friendly design and transit-oriented planning; international research is driven by technological innovation, integrating deep learning, semantic segmentation and other methods, and focusing on climate resilience, equity and mobility complexity. The study divided ABM applications into five core areas and pointed out the differences in data input and implementation strategies between the two, but both recognized the value of ABM in transportation planning, public health and low-carbon city construction. At the same time, the study clarified key challenges such as data scarcity, algorithm limitations, and ethical concerns, and proposed future research directions, including multimodal data fusion, integration with extended reality, and the development of privacy-preserving cross-cultural modeling standards, thereby highlighting the potential of ABM as a smart city simulation tool in promoting adaptive, human-centered, and sustainable neighborhood planning.

Bridging Global Perspectives: A Comparative Review of Agent-Based Modeling for Block-Level Walkability in Chinese and International Research
链接全球视角:中国和国际研究中基于主体的街区级步行性建模的比较回顾
1. Introduction and Research Background
1.1. Research on Block-Level Walkability
1.2. Methods for Assessing Block-Level Walkability
2. Data Sources and Methodology
2.1. Bibliometric Method
2.2. Data Source
3. Comparative Analysis of Chinese and International Literature on ABM, Walkability, and Block-Scale Research
3.1. Comparative Analytical Framework
3.2. ABM Research at the Block Scale: Trends and Regional Perspectives
3.2.1. Trends in Annual Publications
3.2.2. Thematic Focus and Keyword Patterns
3.2.3. Cross-Regional Comparison and Shared Research Priorities
3.3. ABM-Driven Walkability Research: Thematic Evolution and Cross-Cultural Comparison
3.3.1. Trends in Annual Publications
3.3.2. Comparative Keyword Analysis
3.3.3. Cross-Cultural Insights and Methodological Reflections
3.4. Walkability at the Block Scale: Spatial Features and Analytical Focus 3.4.1. Trends in Annual Publications
3.4.2. Spatial Themes and Methodological Patterns
3.4.3. Comparative Summary and Emerging Trends
4. Application Domains and Practical Implications of ABM
4.1. Urban Transportation Planning
4.2. Urban Planning and Design
4.3. Environment and Sustainable Development
4.4. Public Health
4.5. Socio-Economic Analysis
4.6. Feasibility and Limitations of ABM
5. Conclusions and Future Research Directions
研究内容
Research contents
该研究围绕 2015-2024 年基于主体建模(ABM)的街区尺度步行性展开,聚焦中外研究差异,核心探讨 ABM 在街区步行性模拟与优化中的应用。研究首先梳理街区尺度步行性研究的多维度特征,包括空间尺度、安全韧性、感知体验、适老化设计等,指出当前研究存在从静态空间分析向动态行为模拟转变的趋势,但多因素协调与时空行为建模准确性仍待提升;接着对比中外 ABM 应用的侧重点,中国研究呈政策驱动特征,紧扣 “15 分钟社区生活圈” 等国家规划,聚焦社区更新、适老化设计及公交导向规划,国际研究则以技术创新为核心,整合深度学习、语义分割等技术,关注气候韧性、公平性与流动性复杂性;同时,研究明确 ABM 在城市交通、城市设计、环境可持续性、公共卫生、社会经济分析五大领域的应用场景,并分析 ABM 应用面临的数据稀缺、算法局限、伦理担忧等挑战,最终提出多模态数据融合、与扩展现实结合等未来研究方向。
This research focuses on the block-scale walkability based on agent modeling (ABM) from 2015 to 2024. It focuses on the differences between Chinese and foreign research and focuses on the application of ABM in the simulation and optimization of block walkability. The study first sorted out the multi-dimensional characteristics of block-scale walkability research, including spatial scale, safety resilience, sensory experience, aging-friendly design, etc., and pointed out that there is a trend in current research to shift from static spatial analysis to dynamic behavior simulation, but the accuracy of multi-factor coordination and spatiotemporal behavior modeling still needs to be improved. Then, comparing the focus of ABM applications at home and abroad, Chinese research is policy-driven, closely following the "15-minute community living circle" and other national plans, focusing on community renewal, aging-friendly design and transit-oriented planning. International research focuses on technological innovation, integrates deep learning, semantic segmentation and other technologies, and focuses on climate resilience, equity and mobility complexity. At the same time, the study clarifies the application scenarios of ABM in the five fields of urban transportation, urban design, environmental sustainability, public health, and socioeconomic analysis, and analyzes ABM The application faces challenges such as data scarcity, algorithm limitations, and ethical concerns, and ultimately proposes future research directions such as multi-modal data fusion and combination with extended reality.
研究方法
Research methods
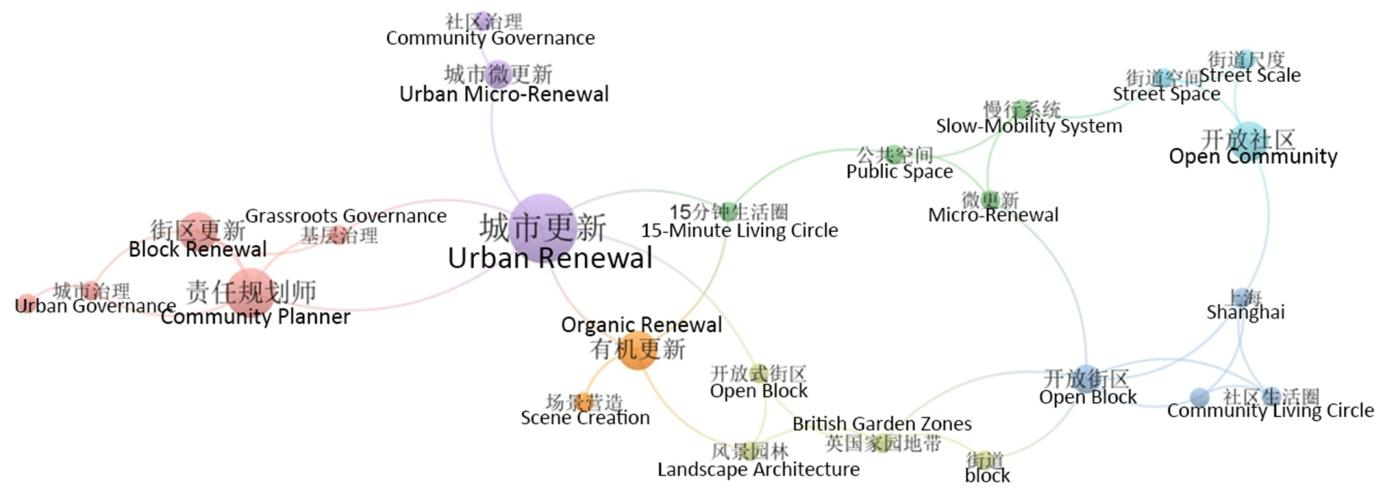
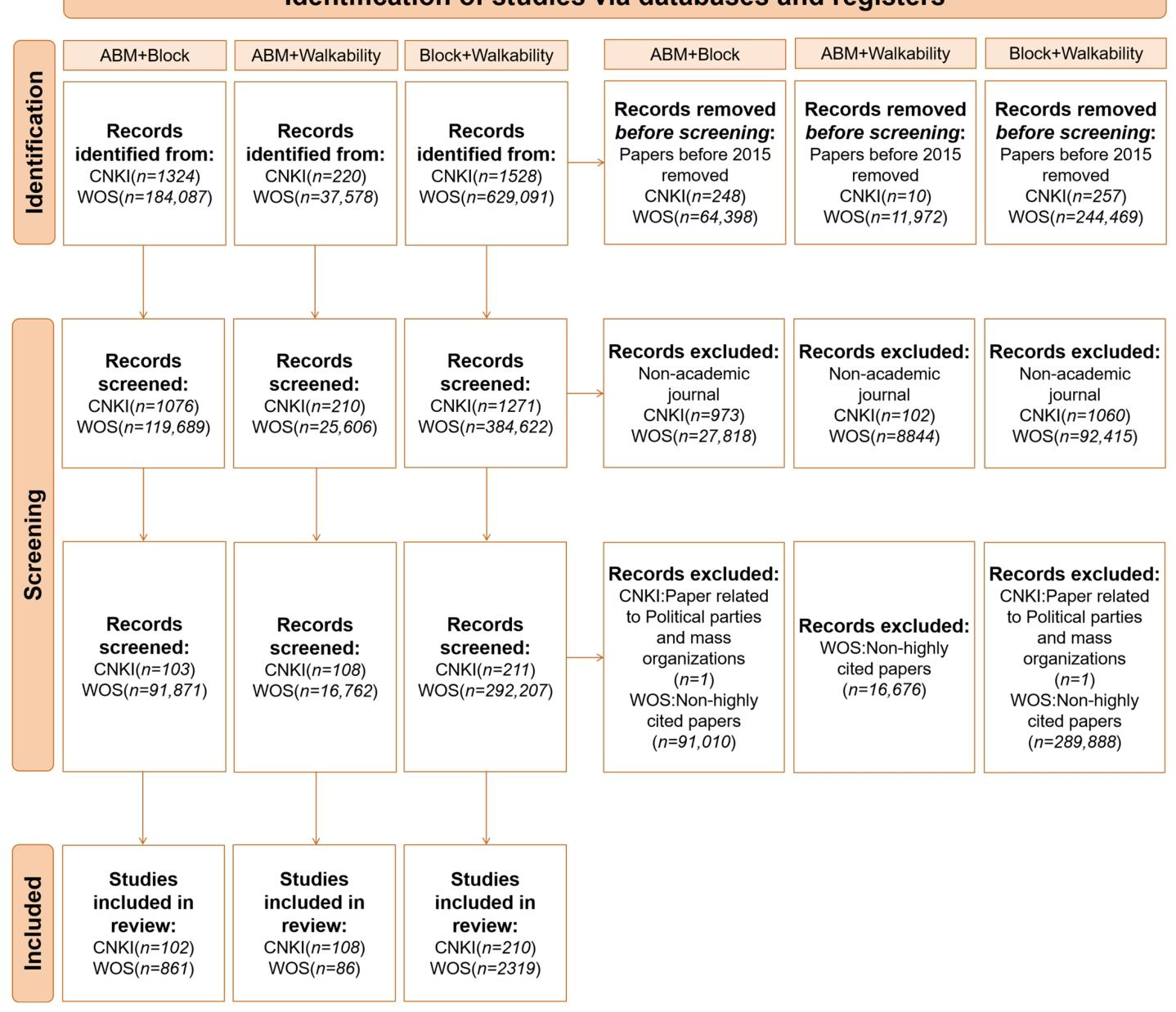
研究采用文献计量法,以 ABM、街区尺度、步行性为核心概念,从中国知网(CNKI)和 Web of Science(WoS)数据库收集 2015-2024 年相关文献,通过 “去重与排除非学术 / 无关文献 — 剔除时间范围外文献 — 人工筛选标题与摘要” 三阶段筛选确定最终分析样本;借助 VOSviewer 工具生成关键词共现图谱,可视化研究热点与主题关联,通过节点大小、位置、颜色分别反映关键词频率、中心性与聚类归属;构建 “城市形态类型学 — 治理模式 — 技术成熟度 — 文化制度导向” 四维比较框架,系统分析中外研究在研究热点、方法路径等方面的差异,同时结合具体案例评估 ABM 在不同领域的应用效果,以此实现对 ABM 在街区步行性研究中应用的全面分析。
The study adopts bibliometric methods, with ABM, neighborhood scale, and walkability as the core concepts, and collects relevant documents from 2015 to 2024 from the China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) and Web of Science (WoS) databases, and determines the final analysis sample through a three-stage screening of "removal and exclusion of non-academic/irrelevant literature - elimination of literature outside the time range - manual screening of titles and abstracts"; with the help of VOSviewer The tool generates a keyword co-occurrence map, visualizes research hotspots and topic associations, and reflects keyword frequency, centrality, and clustering attribution through node size, location, and color. It constructs a four-dimensional comparison framework of "urban morphology typology—governance model—technical maturity—cultural system orientation" to systematically analyze the differences between Chinese and foreign studies in research hotspots, method paths, etc., and evaluate ABM based on specific cases. Application effects in different fields to achieve a comprehensive analysis of the application of ABM in neighborhood walkability research
研究结果
Research conclusions
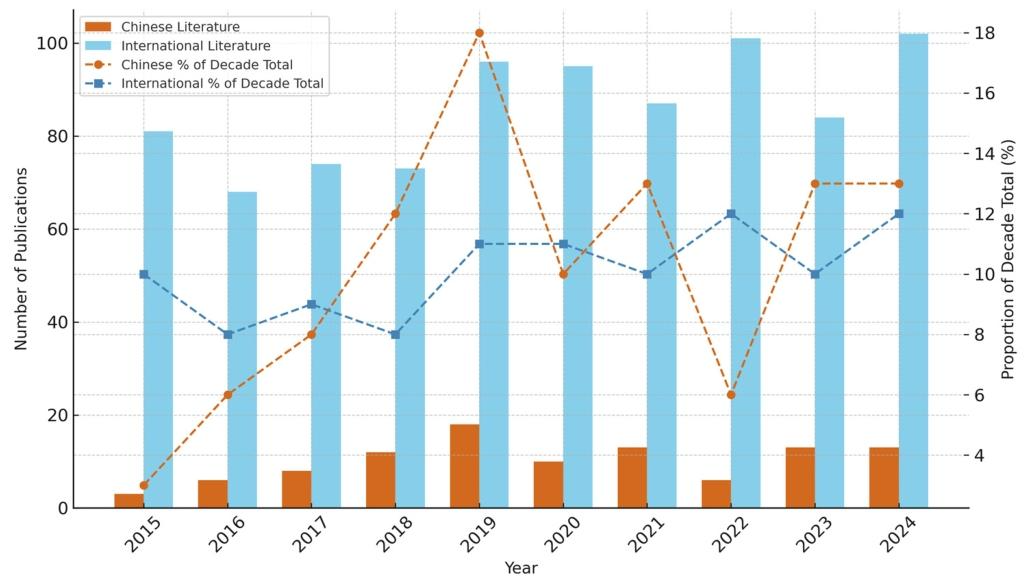
该研究结果显示,2015-2024 年中外基于主体建模(ABM)的街区尺度步行性研究均呈增长态势,中国研究虽起步基数低但增速快,国际研究总量更大且增长稳定,在步行性研究领域,中国 2017-2023 年的年度出版物数量持续高于国际,2020、2023 年达峰,国际研究则在 2015-2020 年稳步增长后于 2021 年后略有下降;研究热点上,中国聚焦政策落地与实践应用,关键词集中于 “城市更新”“15 分钟生活圈”“适老化改造” 等,强调空间公平与设施优化,国际侧重技术创新与伦理反思,围绕 “深度学习”“自动驾驶”“数据隐私”“环境正义” 等展开,注重微观行为模拟与跨学科整合;ABM 在动态模拟行人行为、优化街区设计、支持多场景决策等方面价值显著,可服务于交通规划、环境改善、公共健康等领域,但存在模型校准难、计算成本高、数据隐私风险大、结果可复现性不足等局限;中外研究均认可 ABM 在低碳城市、以人为本规划中的作用,且均关注多源数据融合需求,未来需推动 ABM 从静态规则模型向智能数据融合系统升级,强化气候韧性与人文关怀,构建跨学科、参与式研究生态。
The results of this study show that both Chinese and foreign block-scale walkability research based on agent modeling (ABM) showed a growth trend from 2015 to 2024. Although Chinese research started from a low base, it grew rapidly, and the total amount of international research was larger and the growth was stable. In the field of walkability research, China's annual publication number from 2017 to 2023 continued to be higher than that of the international one, peaking in 2020 and 2023, while international research increased steadily from 2015 to 2020. There will be a slight decline after 2021; in terms of research hotspots, China focuses on policy implementation and practical application, with keywords focusing on "urban renewal", "15-minute living circle", "age-appropriate renovation", etc., emphasizing spatial equity and facility optimization, while the international focus is on technological innovation and ethical reflection, focusing on "deep learning", "autonomous driving", "data privacy" and "environmental justice" etc., focusing on microscopic behavior simulation and interdisciplinary integration; ABM is of significant value in dynamic simulation of pedestrian behavior, optimizing block design, and supporting multi-scenario decision-making, and can serve fields such as transportation planning, environmental improvement, and public health. However, it has limitations such as difficulty in model calibration, high computational costs, high data privacy risks, and insufficient reproducibility of results. Both Chinese and foreign studies recognize the role of ABM in low-carbon cities and people-centered planning, and all focus on the need for multi-source data fusion. ABM needs to be promoted in the future. Upgrading from static rule models to intelligent data fusion systems, strengthening climate resilience and humanistic care, and building an interdisciplinary and participatory research ecosystem