This article focuses on the application of virtual reality (VR) technology in the study of pedestrian emotion perception in urban built environments, and conducts a comparative review of 37 Chinese documents and 113 English documents in the China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) and Web of Science (WOS) databases from 2015 to 2024. The study used a combination of bibliometric analysis (with the help of CiteSpace tools) and qualitative analysis to sort out the publication trends, research hotspots, disciplinary networks and cooperation models of the two types of literature: Chinese literature focused more on embodied cognition and electroencephalography (EEG) monitoring, while English literature focused on the application of VR in stress recovery and health assessment. It was also found that although Chinese research has grown rapidly in recent years, international cooperation is insufficient, and English research started earlier and was more geographically distributed. On this basis, the article proposes a "sensory-cognitive-emotion" framework and spatial intervention strategies, reveals the transformation of urban planning from an engineering orientation to a people-centered model, and also discusses the application potential and limitations of VR technology in neuroscience, public health and other fields (such as ecological validity, hardware compatibility issues), and provides directions for future cross-platform data standardization, cross-cultural research and the establishment of ethical norms, laying a theoretical and methodological foundation for subsequent research in the intersection of immersive technology, built environment research and urban emotional well-being.

Pedestrian Emotion Perception in Urban Built Environments Based on Virtual Reality Technology: A Comparative Review of Chinese- and English-Language Literature
基于虚拟现实技术的城市建成环境中的行人情感感知:中英文文献比较研究
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Data
2.1. Research Framework
2.2. Methods
2.3. Data Source
3. Analysis of Chinese-Language and English-Language Research Status
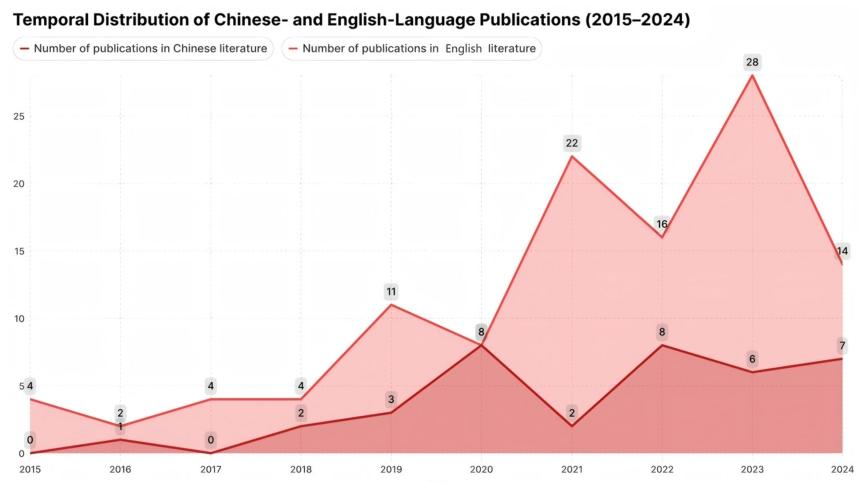
3.1. Temporal Distribution of Publications
3.2. Major Research Contributors and Collaboration Networks
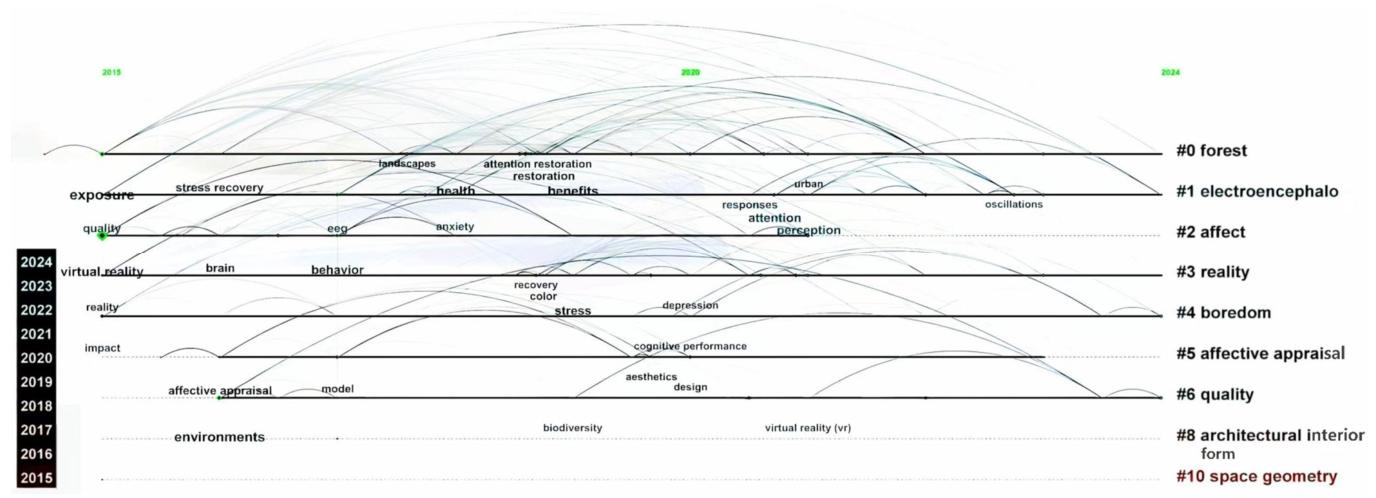
3.3. Research Hotspots and Development Trends
3.3.1. Research Hotspots
3.3.2. Development Trends
3.4. Similarities and Differences Between Chinese-Language and English-Language Literature
4. Discussion
4.1. Mechanism Linking Built Environment and Emotional Feedback
4.2. Spatial Intervention Design Strategies
4.3. Macro-Level Policy Development
4.4. Applications and Prospects of Virtual Reality Technology
5. Conclusions and Future Envision
研究内容
Research contents
该研究聚焦虚拟现实(VR)技术在城市建成环境行人情绪感知领域的应用,通过对比 2015-2024 年中文(CNKI 数据库,37 篇)与英文(WOS 数据库,113 篇)文献,核心探究三方面内容:一是两类文献的研究热点差异,中文文献侧重具身认知、脑电图(EEG)监测及疗愈环境设计,英文文献聚焦 VR 在压力恢复、健康评估及公共政策评估中的应用;二是 VR 技术如何通过 “感官 - 认知 - 情感” 机制链接建成环境与行人情绪反馈,并基于此提出空间干预策略(如街道元素量化调整、文化符号情感转化);三是 VR 技术在宏观城市政策中的应用,包括支持循证决策、构建协同治理框架及智能监测系统,推动城市规划从工程导向向以人为本模式转变,同时探讨 VR 技术的应用局限(如生态效度不足、硬件兼容性问题)与未来跨学科发展方向(如结合神经科学、公共卫生)。
This study focuses on the application of virtual reality (VR) technology in the field of pedestrian emotion perception in urban built environments. By comparing Chinese (CNKI database, 37 articles) and English (WOS database, 113 articles) literature from 2015 to 2024, the core exploration is three aspects: First, the differences in research hotspots between the two types of literature. The Chinese literature focuses on embodied cognition, electroencephalography (EEG) monitoring and healing environment design, while the English literature focuses on VR Application in stress recovery, health assessment and public policy evaluation; second, how VR technology links the built environment and pedestrian emotional feedback through the "sensory-cognitive-emotion" mechanism, and based on this, spatial intervention strategies are proposed (such as quantitative adjustment of street elements, emotional transformation of cultural symbols); third, VR The application of technology in macro-urban policies, including supporting evidence-based decision-making, building collaborative governance frameworks and intelligent monitoring systems, promoting the transformation of urban planning from engineering-oriented to people-oriented models, while exploring the application limitations of VR technology (such as insufficient ecological validity, hardware compatibility issues) and future interdisciplinary development directions (such as combining neuroscience and public health)
研究方法
Research methods
研究采用 “文献计量分析 + 定性分析” 的双方法框架:首先从 CNKI 和 WOS 数据库检索文献,通过筛选(排除非期刊文献、限定学科领域)确定最终研究样本;其次借助 CiteSpace 工具进行文献计量分析,生成作者合作网络、关键词共现图谱、国家 / 机构 publication 分布等可视化结果,梳理发表趋势、研究热点及合作模式;最后基于可视化结果开展定性分析,深入解读中英文文献的主题差异、VR 技术应用逻辑及 “感官 - 认知 - 情感” 机制的理论与实践价值,同时结合具体案例(如 VR 虚拟公园干预抑郁症、地下商业街空间模拟)验证研究结论。
The study adopted a dual-method framework of "bibliometric analysis + qualitative analysis": first, the literature was retrieved from CNKI and WOS databases, and the final research sample was determined through screening (excluding non-journal documents and limiting subject areas); secondly, the CiteSpace tool was used to conduct bibliometric analysis, and visual results such as author collaboration network, keyword co-occurrence map, and country/institution publication distribution were generated to sort out publication trends, research hotspots, and cooperation models; finally, qualitative analysis was conducted based on the visual results to deeply interpret the topic differences between Chinese and English literature, the application logic of VR technology, and The theoretical and practical value of the "sensory-cognitive-emotion" mechanism, and combined with specific cases (such as VR virtual park intervention for depression, underground commercial street space simulation) to verify the research conclusions

研究结果
Research conclusions
该研究的结果显示,在文献特征与合作网络方面,英文文献起步早、数量多(113 篇),2019 年后增长显著且地理分布广泛,但国际合作松散;中文文献虽起步晚(2018 年后增长)、数量少(37 篇),国内机构(如同济大学建筑与城市规划学院)协作紧密,不过中国在该领域的研究虽 publication 量居首但国际合作中心性低于美国。在研究热点上,中文文献高频关键词为 “虚拟现实”“疗愈环境”“EEG 信号”“具身认知”,侧重生理监测与疗愈设计;英文文献核心关键词为 “虚拟现实”“压力恢复”“健康”“感知”,侧重健康影响与政策应用,且主题间关联性较弱(关键词网络密度更低)。理论与实践层面,研究提出 “感官刺激 - 认知评估 - 情感响应” 的环境 - 情绪作用机制,明确 VR 技术在变量隔离、多源数据整合中的关键作用,形成了可落地的空间干预策略(如通过 VR 模拟优化街道绿视率、扶手高度)与政策工具(如 VR 场景模拟辅助公众参与决策),同时指出 VR 需通过多感官设备(如触觉手套、嗅觉发生器)提升生态效度,且需建立跨平台数据标准与伦理规范,整体揭示了城市规划从工程导向向以人为本模式的转变趋势。
The results of this study show that in terms of literature characteristics and cooperation networks, English literature started early and was large in number (113 articles), and grew significantly after 2019 and was widely distributed geographically, but international cooperation was loose. Although Chinese literature started late (increased after 2018) and was small in number (37 articles), domestic institutions (such as the School of Architecture and Urban Planning of Ji University) collaborate closely. However, although China ranks first in the number of publications in this field, the centrality of international cooperation is lower than that of the United States. Regarding research hotspots, the high-frequency keywords in Chinese literature are “virtual reality”, “healing environment”, “EEG signal” and “embodied cognition”, focusing on physiological monitoring and healing design; the core keywords in English literature are “virtual reality”, “stress recovery”, “health” and “perception”, focusing on health effects and policy applications, and the correlation between topics is weak (the keyword network density is lower). At the theoretical and practical level, the study proposed the environment-emotion mechanism of "sensory stimulation-cognitive evaluation-emotional response", clarified the key role of VR technology in variable isolation and multi-source data integration, and formed implementable spatial intervention strategies (such as optimizing street green visibility and handrail height through VR simulation) and policy tools (such as VR scene simulation to assist public participation in decision-making). It also pointed out that VR Ecological validity needs to be improved through multi-sensory devices (such as tactile gloves, olfactory generators), and cross-platform data standards and ethical norms need to be established. This overall reveals the transformation trend of urban planning from engineering-oriented to people-oriented model.